Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM49DUI)
| Drug Name |
Tretinoin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Retinoic acid; tretinoin; 302-79-4; Vitamin A acid; all-trans-Retinoic acid; trans-Retinoic acid; ATRA; Airol; Retin-A; Vesanoid; Renova; Dermairol; Aknoten; Eudyna; Aberel; all-trans-Vitamin A acid; Aknefug; All-trans Retinoic Acid; Cordes vas; Epi-aberel; Atralin; Vitamin A1 acid, all-trans-; Tretin M; Retin-A Micro; all-trans-Vitamin A1 acid; Vitamin A acid, all-trans-; all-trans-Tretinoin; Effederm; Retionic acid; TRETINON; Retinoic acid, all-trans-; Alltrans-retinoic acid; beta-Ra; all-(E)-Retinoic acid; beta-Retinoic acid; Avitoin; Aberela; Acnavit; Atragen; Betarretin; Lsotretinoin; Nexret; Panretyn; REA; Retacnyl; Retinoate; Retinova; Solage; Tretinoina; Tretinoine; Tretinoino; Tretinoinum; Vesnaroid; Vitinoin; Aberela [Norway]; Accutane Roche; Acnavit [Denmark]; All Trans Retinoic Acid; Avita Gel; Avitoin [Norway]; Beta all trans Retinoic Acid; Cordes VAS [Germany]; Effederm [France]; Panretin Gel; Retin A; Trans Retinoic Acid; Tretinoin Potassium Salt; Tretinoin Sodium Salt; Tretinoin Zinc Salt; Tretinoin liposome; AGN100335; AGN 192013; ALRT 1057; BAL4079; LGD 100057; R 2625; [3H]Retinoic acid; A-Vitaminsyre; A-Vitaminsyre [Denmark]; AT-RA; Aberela (TN); Acid, Retinoic; Acid, Vitamin A; All trans-Retinoic acid; Atra-IV; Avita (TN); B-Retinoic acid; BML2-E05; Beta-Ra; Beta-Retinoic acid; Potassium Salt, Tretinoin; RETINOIC ACID, ALL TRANS; Renova (TN); Retin A (TN); Retisol-A; Ro 1-5488; Salt, Tretinoin Potassium; Salt, Tretinoin Sodium; Salt, Tretinoin Zinc; Sodium Salt, Tretinoin; Stieva-A; Stieva-a Forte; Trans-Retinoicacid; Tretinoin (TN); Tretinoina [INN-Spanish]; Tretinoine [INN-French]; Tretinoino [INN-Spanish]; Tretinoinum [INN-Latin]; Tri-Luma; Vesanoid (TN); Zinc Salt, Tretinoin; A-Acido (Argentina); Acid A Vit (Belgium, Netherlands); Acid, trans-Retinoic; Acide retinoique (French) (DSL); All-trans-Retinoic acid; All-trans-Tretinoin; All-trans-Vitamin A acid; All-trans-Vitamin A1 acid; PDT-002-002; Retin-A (TN); Stieva-A (TN); Tretinoin 01% cream or placebo; Tretinoin [USAN:INN:BAN]; Tretinoin/All-Trans Retinoic Acid; Tretinoine (French) (EINECS); Acid, all-trans-Retinoic; All-(E)-Retinoic acid; All-trans-b-Retinoic acid; All-trans-beta-Retinoic acid; Beta-all-trans-Retinoic acid; Tretinoin (JAN/USP/INN); Acid, beta-all-trans-Retinoic; Retinoic acid, all-trans-(8CI); Vesanoid, Airol, Renova, Atralin, Retin-A, Avita, Tretinoin; 15-Apo-beta-caroten-15-oic acid; 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid; 9(Z)-Retinoic acid; 9-cis-RA; 9-trans-retinoic acid
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Keratolytic Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
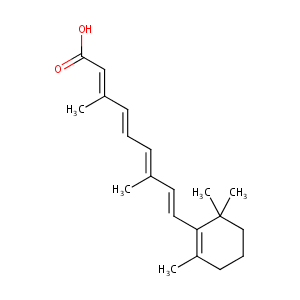 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 300.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 6.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Acne vulgaris | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | ED80 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Tretinoin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Tretinoin (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
| DIG |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Formulation |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2644). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Tretinoin FDA Label | ||||
| 3 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | Retinoids--which dermatological indications will benefit in the near future Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 2001 Sep-Oct;14(5):303-15. | ||||
| 8 | Targacept active conformation search: a new method for predicting the conformation of a ligand bound to its protein target. J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 30;47(27):6831-9. | ||||
| 9 | Carotenoids reverse multidrug resistance in cancer cells by interfering with ABC-transporters. Phytomedicine. 2012 Aug 15;19(11):977-87. | ||||
| 10 | Identification of human cytochrome P450s involved in the formation of all-trans-retinoic acid principal metabolites. Mol Pharmacol. 2000 Dec;58(6):1341-8. | ||||
| 11 | Summary of information on human CYP enzymes: human P450 metabolism data. Drug Metab Rev. 2002 Feb-May;34(1-2):83-448. | ||||
| 12 | CYP26C1 is a hydroxylase of multiple active retinoids and interacts with cellular retinoic acid binding proteins. Mol Pharmacol. 2018 May;93(5):489-503. | ||||
| 13 | Transcriptional and Metabolic Dissection of ATRA-Induced Granulocytic Differentiation in NB4 Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Cells. Cells. 2020 Nov 5;9(11):2423. doi: 10.3390/cells9112423. | ||||
| 14 | Effect of retinoic acid on gene expression in human conjunctival epithelium: secretory phospholipase A2 mediates retinoic acid induction of MUC16. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Nov;46(11):4050-61. | ||||
| 15 | Development of a neural teratogenicity test based on human embryonic stem cells: response to retinoic acid exposure. Toxicol Sci. 2011 Dec;124(2):370-7. | ||||
| 16 | Differential modulation of PI3-kinase/Akt pathway during all-trans retinoic acid- and Am80-induced HL-60 cell differentiation revealed by DNA microarray analysis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Dec 1;68(11):2177-86. | ||||
| 17 | Phenotypic characterization of retinoic acid differentiated SH-SY5Y cells by transcriptional profiling. PLoS One. 2013 May 28;8(5):e63862. | ||||
| 18 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 19 | Gardner K, Cox T, Digre KB "Idiopathic intracranial hypertension associated with tetracycline use in fraternal twins: case reports and review." Neurology 45 (1995): 6-10. [PMID: 7824136] | ||||
| 20 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Multaq (dronedarone). sanofi-aventis , Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 23 | Adamson PC "Pharmacokinetics of all-trans-retinoic acid: clinical implications in acute promyelocytic leukemia." Semin Hematol 31 (1994): 14-7. [PMID: 7831580] | ||||
| 24 | Johnson EJ, MacGowan AP, Potter MN, et al "Reduced absorption of oral ciprofloxacin after chemotherapy for haematological malignancy." J Antimicrob Chemother 25 (1990): 837-42. [PMID: 2373666] | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Tykerb (lapatinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 27 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Canadian Product Information.". | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Viibryd (vilazodone). Trovis Pharmaceuticals LLC, New Haven, CT. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Trileptal (oxcarbazepine) Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Xcopri (cenobamate). SK Life Science, Inc., Paramus, NJ. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Priftin (rifapentine). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Prezista (darunavir). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 37 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Orladeyo (berotralstat). BioCryst Pharmaceuticals Inc, Durham, NC. | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Alunbrig (brigatinib). Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 42 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Copiktra (duvelisib). Verastem, Inc., Needham, MA. | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Tasigna (nilotinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Sprycel (dasatinib). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 48 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 49 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 51 | Doherty MM, Charman WN "The mucosa of the small intestine: how clinically relevant as an organ of drug metabolism?" Clin Pharmacokinet 41 (2002): 235-53. [PMID: 11978143] | ||||
| 52 | DSouza DL, Levasseur LM, Nezamis J, Robbins DK, Simms L, Koch KM "Effect of alosetron on the pharmacokinetics of alprazolam." J Clin Pharmacol 41 (2001): 452-4. [PMID: 11304902] | ||||
| 53 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
